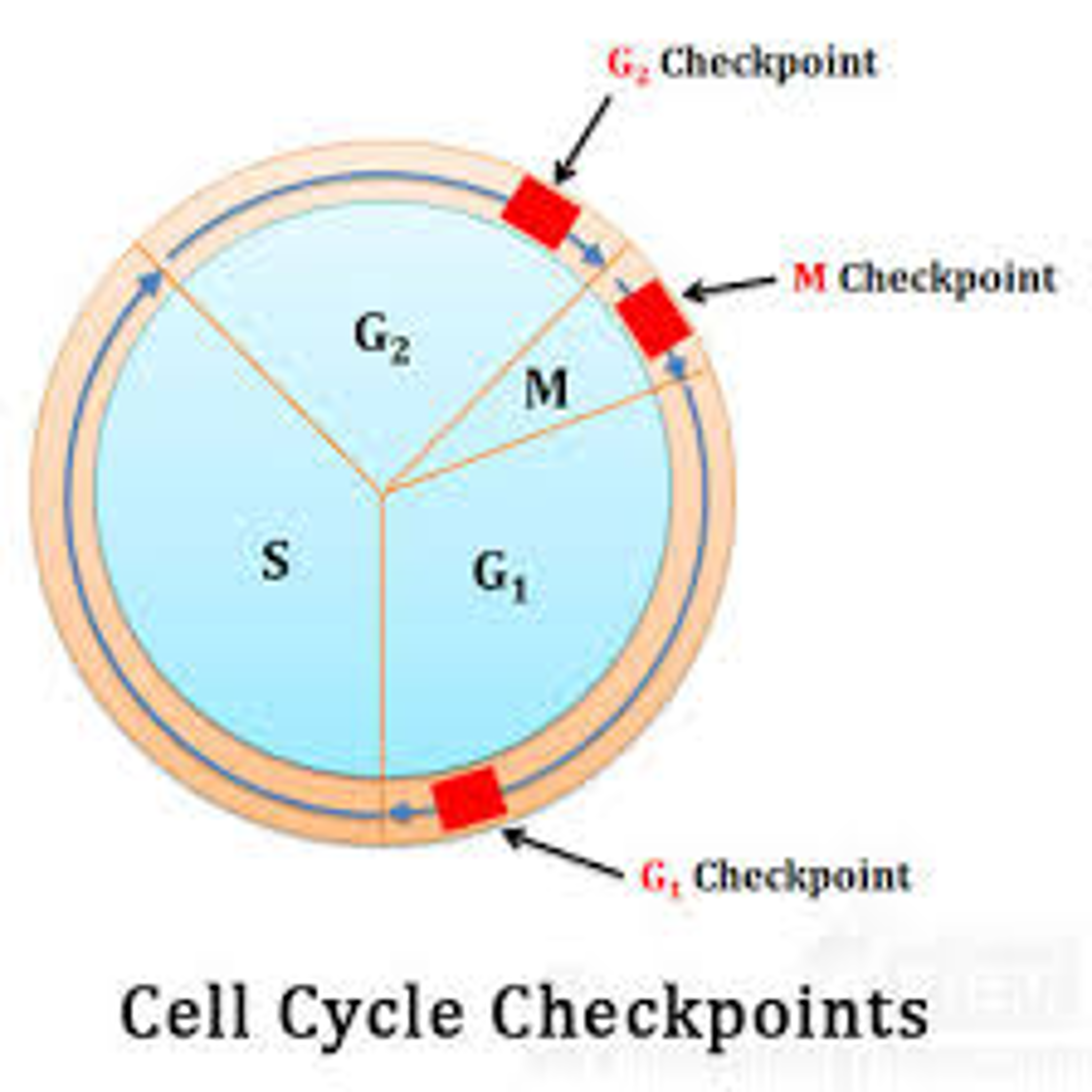
Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary . A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Regulation of the cell cycle. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2.
from mungfali.com
Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Regulation of the cell cycle. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Diagram
Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Regulation of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints.
From mungfali.com
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Diagram Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Regulation of the cell cycle. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.researchgate.net
Regulation of the cell cycle and its checkpoints by specific Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. Proper chromosome duplication. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.biotechfront.com
What are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Biotechfront Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Regulation of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. Each step of the cell. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From quizzlibraryzimmer.z13.web.core.windows.net
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Ppt Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Regulation of the cell cycle. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.youtube.com
G2/M Checkpoint Cell cycle regulation YouTube Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Regulation of the cell cycle. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity,. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From classmediafloyd.z21.web.core.windows.net
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Notes Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From quizlet.com
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Diagram Quizlet Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. Regulation of the cell cycle. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From lookfordiagnosis.com
G2 phase cell cycle checkpoints Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From quizlet.com
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Diagram Quizlet Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From sciencenotes.org
Cell Cycle Phases and Checkpoints Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity,. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.reddit.com
Cell cycle checkpoints r/Conceptofbio Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Regulation of the cell cycle. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.slideshare.net
Cell cycle and its checkpoints Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Regulation of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. There are three major. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From worksheetlibrarysteins.z19.web.core.windows.net
Cell Cycle And Checkpoints Worksheet Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Regulation of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. Proper. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From cellcycleregulation123.blogspot.com
Checkpoints and regulators Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Each. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From quizlet.com
Cell Cycle and Checkpoints (in progress) Diagram Quizlet Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. Regulation of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Biology for Majors I Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. The cell cycle is controlled at three major checkpoints. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From goldbergbrolud.blogspot.com
The G2 Checkpoint Prevents the Cell Cycle From Continuing Until Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted. Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle:. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.
From www.biorender.com
Cell Cycle Checkpoints (Layout) BioRender Science Templates Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the g2. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. There are. Why Are Cell Cycle Checkpoints Necessary.